Understanding COPD Progression: Signs, Stages, and Treatment Options
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive respiratory condition that significantly impacts the quality of life for millions worldwide. Characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation, COPD is primarily caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, most often from cigarette smoke. Understanding the progression and treatment of COPD is crucial.
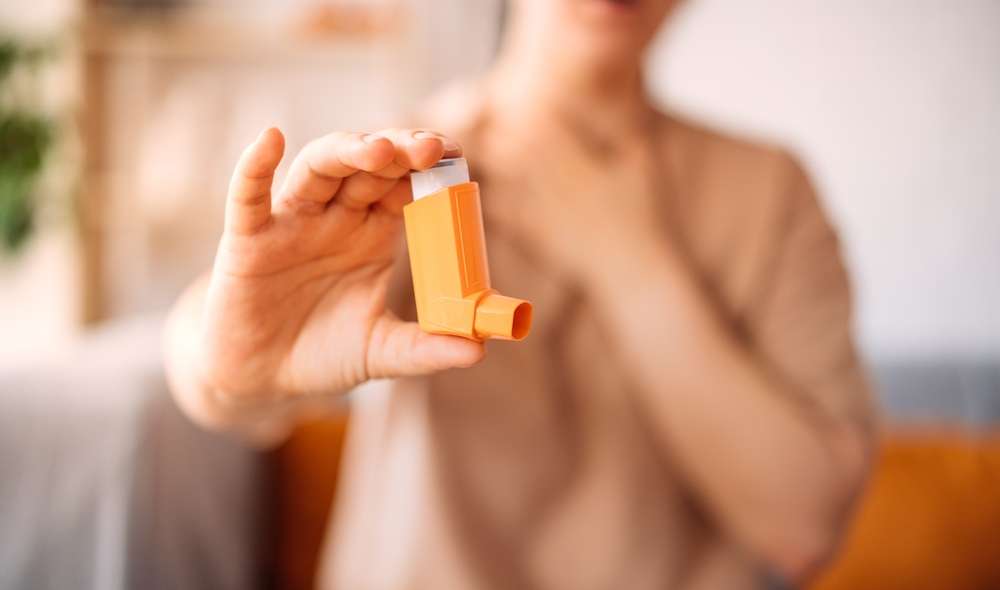

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) represents a significant health challenge, characterized by persistent airflow limitation and breathing difficulties that worsen over time. Understanding how this condition develops and progresses is essential for effective management and maintaining quality of life.
What Are the Symptoms and Treatment of COPD?
COPD manifests through several recognizable symptoms that typically develop gradually. The most common early signs include persistent cough, often producing mucus, shortness of breath during physical activities, wheezing, and chest tightness. As the disease advances, patients may experience increased difficulty breathing even during rest, frequent respiratory infections, fatigue, and unintended weight loss.
Treatment approaches for COPD focus on symptom management, slowing disease progression, and preventing complications. Bronchodilators remain the cornerstone of pharmacological treatment, helping to relax airway muscles and improve breathing. Inhaled corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce airway inflammation, particularly for patients experiencing frequent exacerbations. Pulmonary rehabilitation programs combine exercise training, nutritional counseling, and education to help patients manage symptoms more effectively. Oxygen therapy becomes necessary for advanced stages when blood oxygen levels drop significantly. Lifestyle modifications, especially smoking cessation, represent the most critical intervention for slowing disease progression.
How Does COPD Progress Through Different Stages?
Medical professionals classify COPD into four stages based on lung function measurements and symptom severity. Stage 1, or mild COPD, often goes unnoticed as symptoms remain subtle, with lung function at 80 percent or higher of expected capacity. Patients may experience occasional coughing and mild shortness of breath during strenuous activities.
Stage 2, moderate COPD, presents more noticeable symptoms, with lung function declining to 50-79 percent of normal capacity. Patients typically seek medical attention at this stage due to persistent breathlessness during routine activities and more frequent coughing episodes.
Stage 3, severe COPD, significantly impacts daily life, with lung function dropping to 30-49 percent of expected levels. Breathing difficulties become pronounced even during light activities, and exacerbations occur more frequently, often requiring hospitalization.
Stage 4, very severe COPD, represents the most advanced form, with lung function below 30 percent of normal capacity. Patients experience chronic respiratory failure, severely limited physical capacity, and life-threatening exacerbations. Quality of life diminishes substantially, and survival rates decrease significantly at this stage.
What Are Emerging COPD Treatments in 2025?
The medical community continues developing innovative approaches to COPD management beyond traditional therapies. Targeted anti-inflammatory medications aim to address specific inflammatory pathways involved in COPD progression, potentially reducing exacerbation frequency and slowing lung function decline.
Stem cell research shows promise for regenerating damaged lung tissue, though clinical applications remain largely experimental. Bronchoscopic lung volume reduction procedures offer less invasive alternatives to traditional surgery for select patients with severe emphysema, improving breathing capacity by removing damaged lung tissue.
Advanced digital health technologies, including remote monitoring devices and artificial intelligence-driven symptom tracking, enable earlier detection of exacerbations and more personalized treatment adjustments. Gene therapy research explores possibilities for addressing genetic factors contributing to COPD susceptibility, though practical applications remain years away from widespread availability.
Vaccine development targeting respiratory pathogens that trigger COPD exacerbations represents another promising area, potentially reducing hospitalizations and disease progression rates.
How Does COPD Biologic Injections Therapy Work?
Biologic therapies represent a significant advancement in COPD treatment, particularly for patients with specific inflammatory profiles. These medications target particular molecules involved in the inflammatory process that damages airways and lung tissue.
Eosinophilic COPD, characterized by elevated levels of eosinophils (a type of white blood cell), may respond to biologic injections that block interleukin-5 or its receptor. These treatments reduce eosinophil-driven inflammation, potentially decreasing exacerbation frequency and improving lung function in selected patients.
Biologic therapies typically require subcutaneous injections administered every few weeks, depending on the specific medication. Healthcare providers conduct blood tests and assess inflammatory markers to identify patients most likely to benefit from these treatments. While biologics show promise, they remain reserved for patients with severe COPD who experience frequent exacerbations despite optimal conventional therapy.
Side effects generally remain mild, including injection site reactions and potential increased infection risk. Long-term safety data continues accumulating as these treatments gain wider use in clinical practice.
What New COPD Treatments Are Available in 2025?
Recent therapeutic developments expand options for COPD management beyond established protocols. Combination inhalers incorporating multiple medication classes in single devices improve treatment adherence and symptom control. Triple therapy inhalers, combining long-acting bronchodilators with inhaled corticosteroids, demonstrate superior efficacy for patients with moderate to severe disease.
Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors represent oral medications that reduce inflammation and exacerbation frequency in patients with chronic bronchitis and frequent flare-ups. Mucolytic agents help thin mucus secretions, making clearance easier and reducing infection risk.
Minimally invasive bronchoscopic procedures, including targeted lung denervation and airway bypass techniques, offer symptom relief for carefully selected patients when medications prove insufficient. These interventions aim to reduce airway constriction and improve air trapping without requiring major surgery.
Personalized medicine approaches increasingly guide treatment selection based on individual patient characteristics, inflammatory profiles, and genetic factors, moving away from one-size-fits-all protocols toward tailored therapeutic strategies.
Managing COPD: A Comprehensive Approach
Effective COPD management extends beyond medications to encompass lifestyle modifications, preventive care, and patient education. Regular physical activity, within individual capacity limits, maintains muscle strength and cardiovascular health. Nutritional support addresses weight loss and muscle wasting common in advanced disease stages.
Vaccination against influenza and pneumococcal infections reduces exacerbation risk. Air quality awareness helps patients avoid environmental triggers, including smoke, pollution, and chemical irritants. Breathing techniques and airway clearance methods taught through pulmonary rehabilitation programs enhance daily symptom management.
Psychological support addresses anxiety and depression frequently accompanying chronic respiratory disease, improving overall well-being and treatment adherence. Advance care planning ensures patient preferences guide treatment decisions as disease progresses.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Understanding COPD progression empowers patients and families to recognize warning signs, seek appropriate care, and explore available treatment options. While COPD remains a chronic progressive condition, advances in medical therapy and comprehensive management strategies continue improving outcomes and quality of life for those affected by this respiratory disease.